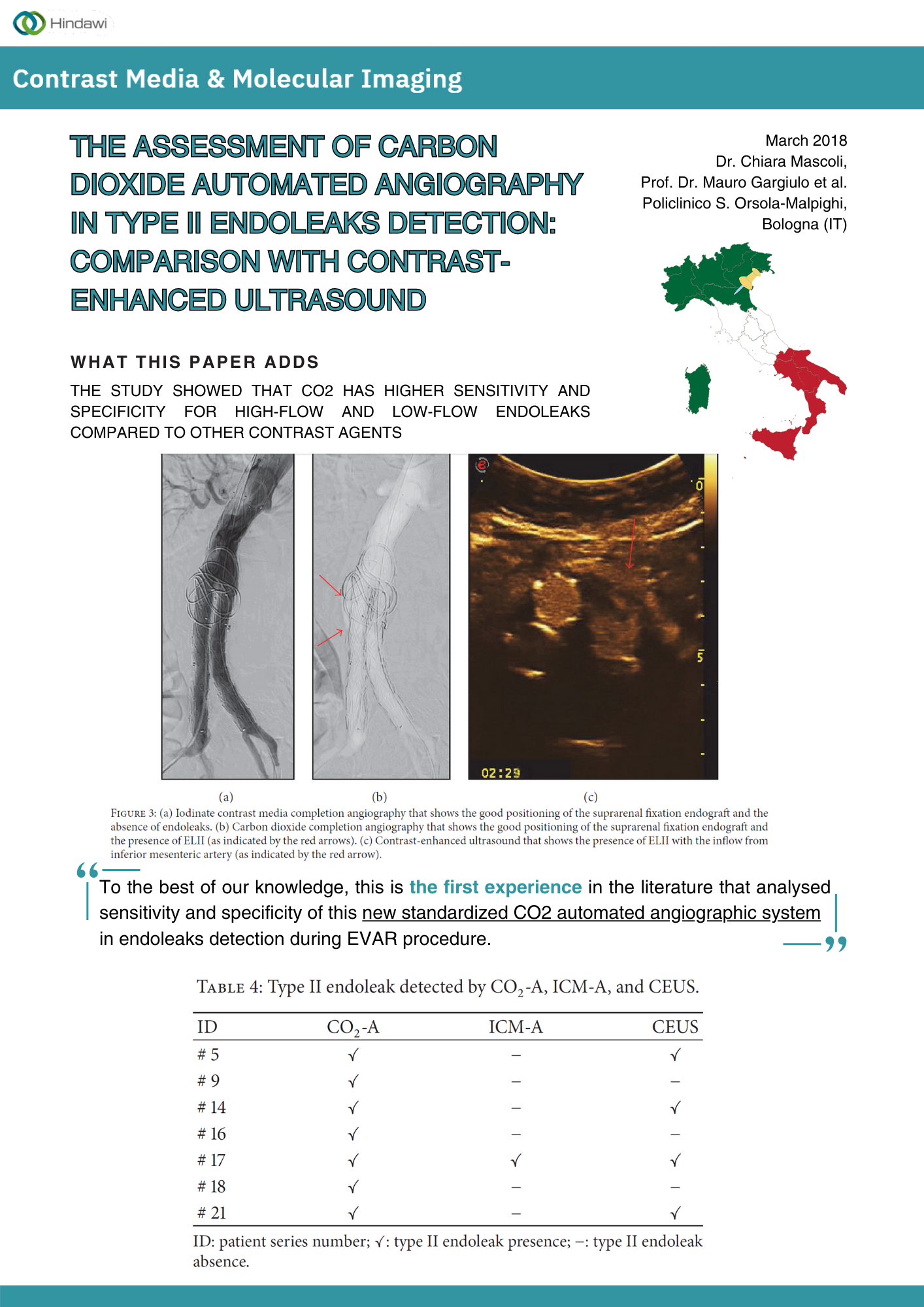
Paper
Image quality and safety of ACDA in lower limbs
Purpose: To evaluate the image quality and the safety of automated carbon dioxide (CO2) digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Materials and Methods: Fifty patients receiving DSA for femoropopliteal peripheral arterial disease (PAD) were enrolled in this single-center prospective study. All patients received iodinated contrast media (ICM) and CO2 as a contrast agent in the same target lesion. As a primary endpoint, four raters independently evaluated the angiography images based on overall image quality, visibility of collaterals, and assessment of stenoses/occlusions. Inter-rater agreement was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and differences between the raters were evaluated using Friedmann’s test. Secondary endpoints were procedure safety and patient pain assessment.
Results: Inter-rater agreement between CO2-DSA and ICM-DSA images was fair to excellent for overall image quality (ICC: 0.399–0.748), fair to excellent for the visibility of collaterals (ICC: 0.513–0.691), and poor to excellent for the assessment of stenoses/occlusions (ICC: -0.065–0.762). There were no significant differences between the raters. Two patients had a hematoma, one reported pain related to puncture, one became nauseous, and one vomited. No other adverse events were observed. Reported pain scores were significantly higher for CO2- DSA vs. ICM-DSA (1.25 vs. 0625; p < 0.028).
Conclusion: CO2-DSA using automated injection system in combination with proprietary post-processing software is safe and comparable diagnostic test compared to ICM-DSA.
Contact us for more information.
.png?width=2000&height=1415&name=Progetto%20senza%20titolo%20(8).png)